What is a URL?
Everything you need to know about URLs
A URL, or Uniform Resource Locator, is the address of a website or web page on the internet. It’s a unique web address that will lead you to a specific webpage. Every page on the internet has its own URL, just like the one you are on now.
URLs are not the same as domain names, but they are related. The domain name is a part of the URL.
In this article, you will learn all there is to know about URLs. We will explain what they are and what they do, how to create them, and some best practices to follow!
Brief Summary
A URL is the web address that you type into your web browser to visit a webpage. It refers to the entire address, including the scheme (“https://”), the domain name and any additional paths, parameters or anchors.
What is a URL and what does it do?
The URL is an important part of a website. It’s what people type into their browser to find your site, and it is what search engines like Google use to index your pages for relevance. URLs are not only necessary for getting found online, but they also work as a way to tell you more about the page that someone wants you to see.
The URL can indicate what the page is about and how it relates to other pages on your site (if there is a subfolder called “/blog/” in the URL, it indicates that the page is a blog article). The URL will also be helpful when linking internally within your own website because it tells users which section of your site you want them to visit next.
To fully understand what a URL is, you need to understand the different parts that make it up. A URL consists of multiple parts.
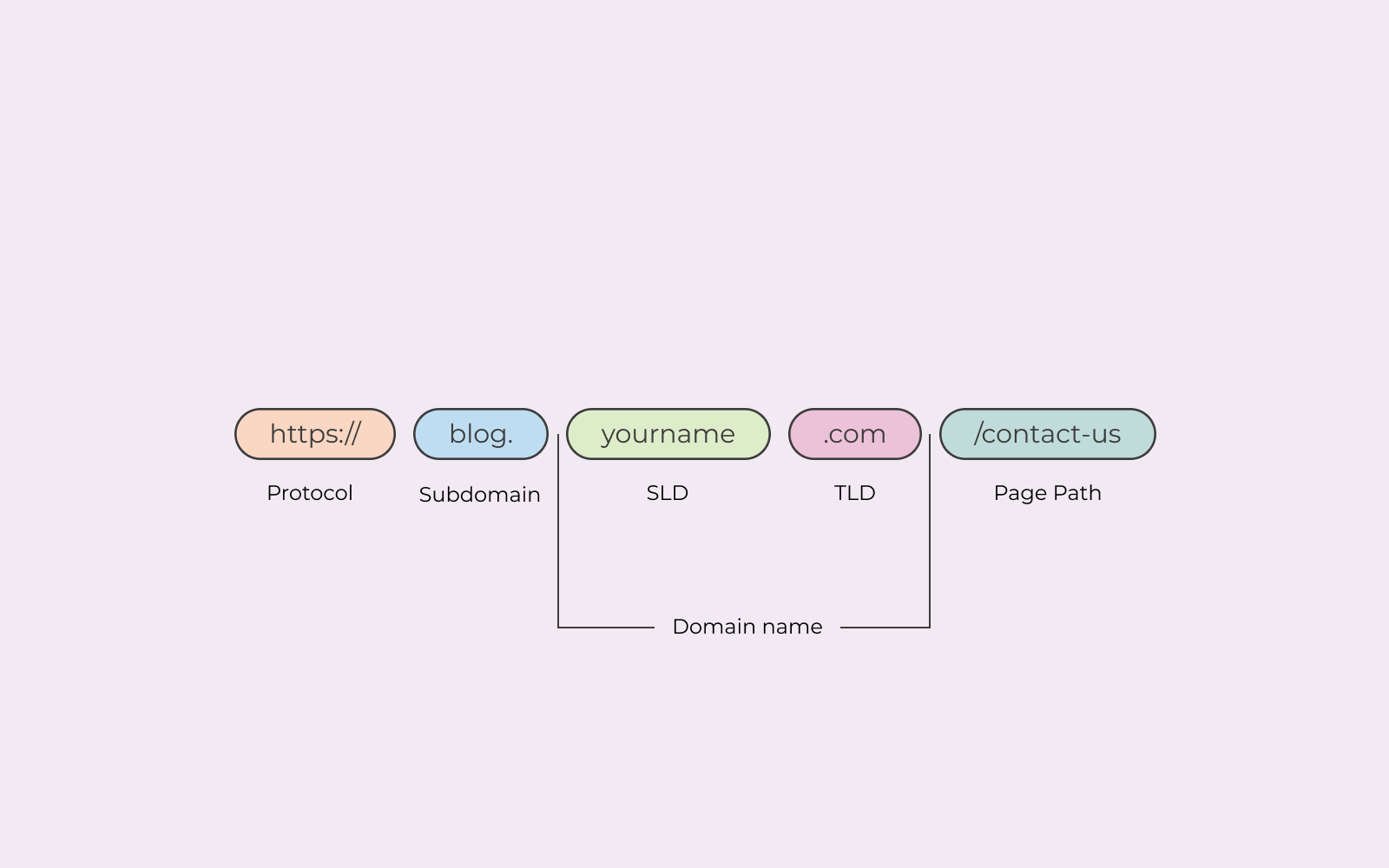
Protocol
The first part of a URL is the scheme, which tells the browser which protocol it must use in order to access the page. In most cases, this is either HTTP or HTTPS.
Subdomain
Subdomains are a way of splitting up a website into different sections. WWW is also considered a subdomain.
Second-level domain
This is basically your domain name, without the top-level domain. In our domain name, “one.com”, the word “one” represents are second-level domain.
Top-level domain
The top-level domain, or domain extension, is the final part of the domain name. For example, .com, .net or .eu.
Path
The path is mostly defined by the URL structure of your website. On this page the path is /en/domain/what-is-a-url.
Page extension
Some URLs have page extensions, like .html. For example, URLs of files and images. An image URL ends with an image extension, like .png.
Parameters & Anchors
A URL can also have a parameter or an anchor. Parameters are a way to add additional information to a specific URL. They can be used for multiple things such as site search or tracking purposes. You can recognise parameters in URLs that have a question mark. The question mark indicates the start of a parameter.
An anchor is a jump link. It starts with a “#”. For example, if you add #what-is-a-url-and-what-does-it-do to the URL of this page, it would bring you back to the first heading.
Tips for ensuring that your URLs are effective and user-friendly
URLs are important for two main reasons: firstly, because they help us organise and find things on the internet; secondly, because they define the URL structure of a website. And having a good URL structure is important to make sure users can easily navigate your site, and for ranking well in search engines.
It’s easier for users to navigate a website with a good URL structure. For example, the path of this page is /en/domain/what-is-an-url. We have put it deliberately in the /en subfolder (because it’s an English page) and the /domain subfolder (because it’s related to domains). All our other domain-related blog articles are located in the same subfolders. Having a logical URL for every page, is a good way to structure your website.
In terms of website performance, URLs are one of the factors that search engines use to rank websites. The better your URLs are – that is, the more relevant and concise they are – the higher you’ll rank in search engine results pages (SERPs). So if you’re looking to improve your website’s SEO, make sure your URLs are as good as they can be!
The most common mistakes people make with their URLs include creating too lengthy URLs, using overly complicated words or phrases that are difficult to remember, and including special characters that can confuse browsers (or worse, search engines).
The domain name is a part of your URLs, so your first step is to buy a domain. Once you have that, and you’re building your website, you can focus your attention on individual URLs.
Here are some tips for creating URLs that will be effective and user-friendly:
- Make a logical URL structure and use subfolders to categorise your content. This can be done in different ways. You could for example place all blog articles under yourwebsite.com/blog and all products under yourwebsite.com/product. You can approach a URL structure in a similar way as a file explorer on your computer. All blog articles will be in the blog folder, and all product pages will be in the product folder.
- Keep your URLs short and sweet. The fewer characters in a URL, the easier it is to remember and type in.
- Try not to use special characters in your URL. If you have to include special characters in your URL, try to use only common ones that won’t cause any confusion.
- Instead of spaces, use hyphens (-). They are both user and search engine friendly, unlike underscores (_).
- Make your URLs future-proof. For example, if you write an article about digital marketing trends for this year, don’t include the year in the URL. Your URL will be outdated soon. Instead, use a URL like /digital-marketing-trends, so you can update the article every year without having to change the URL.
By following these simple tips, you can create URLs that are effective, user-friendly – and best of all – easy for everyone to remember!
Should you change your URLs?
URLs can be changed at any time, but you might confuse users and search engines. This is why it’s so important to have a good URL structure. A good URL structure makes it more likely you don’t have to change your URLs in the future. And with the tips above, you now know how to make a good structure.
But even with a good URL structure, there can always be cases where you need to change the URL of a page. And that’s perfectly fine.
When you do decide to change URLs, it is important to use a 301 redirect. This ensures that users who type in the old URL, are redirected to the new one, thus landing on the new page. If you don’t do this, users will land on a 404 page and will not find what they’re looking for.
301 redirects also help with SEO. It will transfer value from the old to the new URL, minimizing your loss in rankings for that page. Without a redirect, search engines can not make the connection that the URL has changed, and you are much more likely to lose rankings and traffic.
That’s it! Now you know everything you need to know about URLs! And now that you know how you can create good URLs, it’s time to use that knowledge! The next time you are creating a new page or post on your website, take some time to come up with a good URL name that accurately describes the content. And remember, the best URLs are short, simple, and easy to remember.
Do you want to create your own URLs? Register a domain today!
